


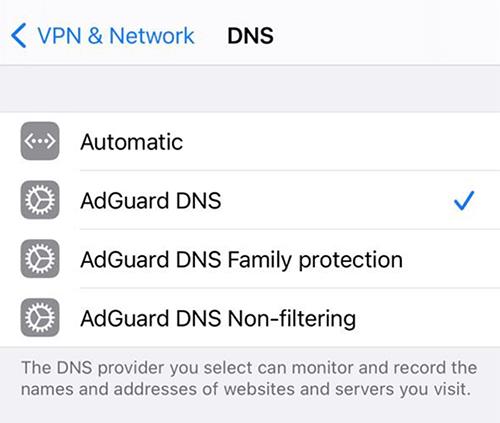
Other DNS providers may work differently, so learn more about them before committing to this or that DNS server. This diagram illustrates how AdGuard blocking servers work: AdGuard has different servers for different goals. AdGuard also provides a DNS service, and it was the world's first to offer the very new and promising DNS-over-QUIC encryption protocol. Nowadays all major DNS servers employ one or more reliable encryption protocols: DNS-over-HTTPS, DNS-over-TLS. Most simply return the IP address of the requested domain, but some have additional functions: they block ad, tracking, adult domains and so on. There are thousands of DNS servers to choose from, and they are all unique in their properties and purposes.
More on that later.ĭNS filtering is a powerful tool and it's supported by all major AdGuard apps: AdGuard for Windows, AdGuard for Mac, AdGuard for Android and AdGuard for iOS.ĭNS filtering can be broken down into two separate functions: to encrypt and reroute DNS traffic to DNS servers, and to block some domains locally by applying DNS blocklists. On top of that, AdGuard can identify requests to ad, tracking, and/or adult domains and redirect them to a "blackhole" instead of forwarding them to the DNS server. AdGuard will encrypt all your DNS requests before they leave your device, so that no malefactor could get access to their contents. If you're using the default DNS server provided by your ISP, your DNS traffic is likely not encrypted and vulnerable to snooping and hijacking. All DNS requests that your browsers or apps are about to send first get processed by AdGuard. When you use one of the AdGuard apps that supports DNS filtering, it acts as a buffer between your device and the DNS server. The same applies, of course, to all apps and programs that send any web requests, not just browsers. Very schematically it can be represented like this: That server looks at the requested domain name and replies with a corresponding IP address.
Thus, each time you go to a website, your browser sends a request to a special type of server (DNS server). What is DNS? ĭNS stands for "Domain Name System", and its purpose is to translate websites' names into something browsers can understand, i.e. To better understand DNS filtering, first, we should answer the question "What is DNS?".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
